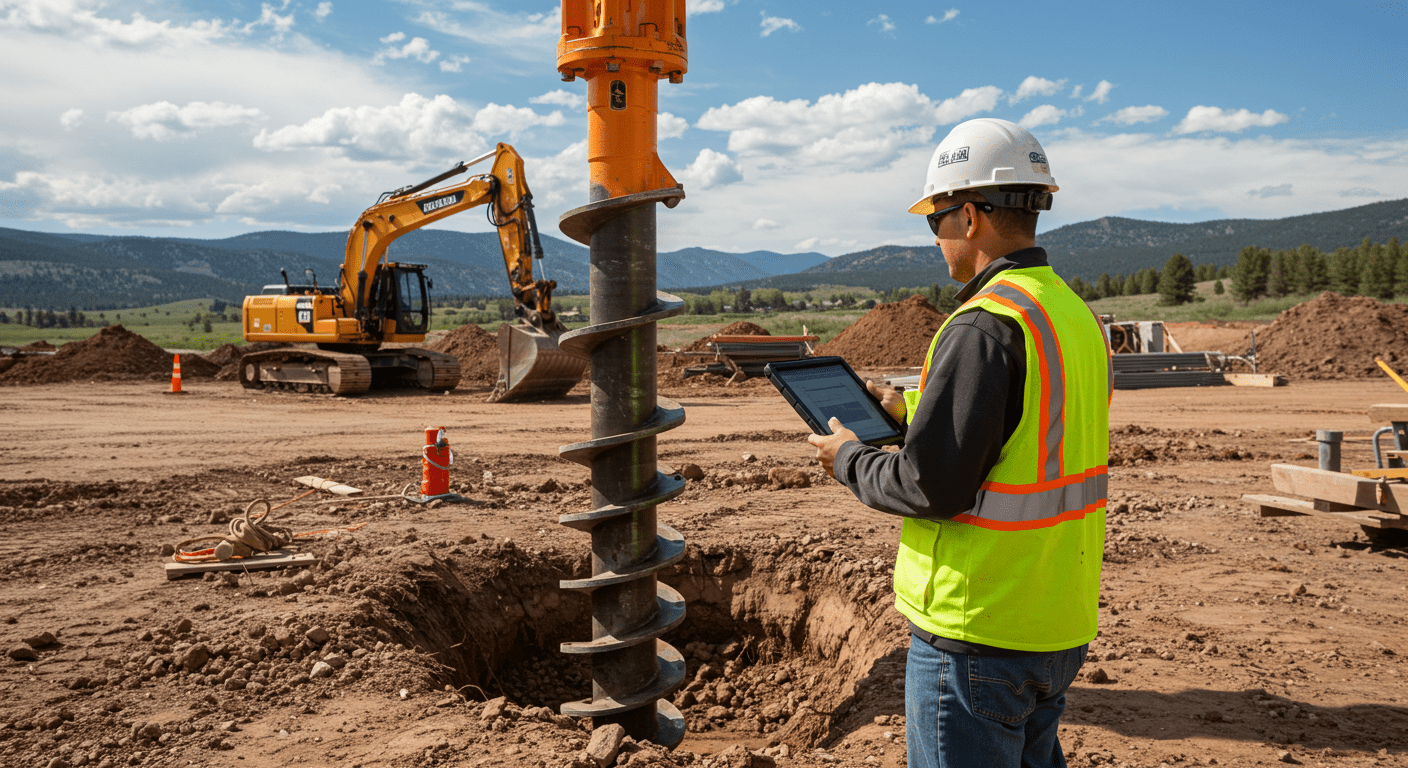
Conquering the Challenge: How Helical Piers Triumph Over Expansive Soil Issues
Eexpansive soil movements can exert tremendous pressure on foundations, leading to structural damage over time. Helical piers, with their ingenious design and installation method, emerge as a powerful solution to combat the problems associated with expansive soils.
Preventing Vertical Movement:
Maintaining Consistent Elevation:
Counteracting Lateral Forces:
Distributing Load Evenly:
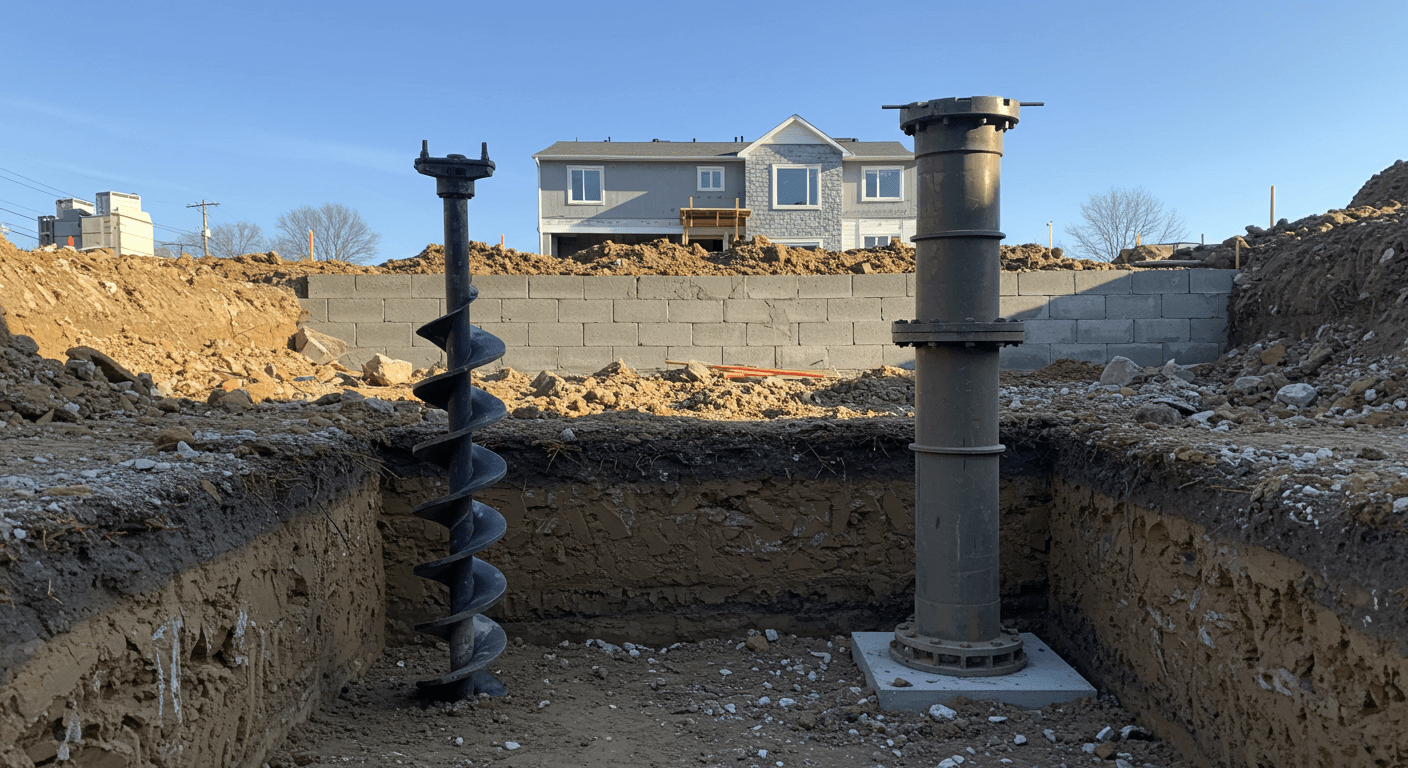
Reaching Stable Soil Strata:
Minimizing Soil Disturbance:
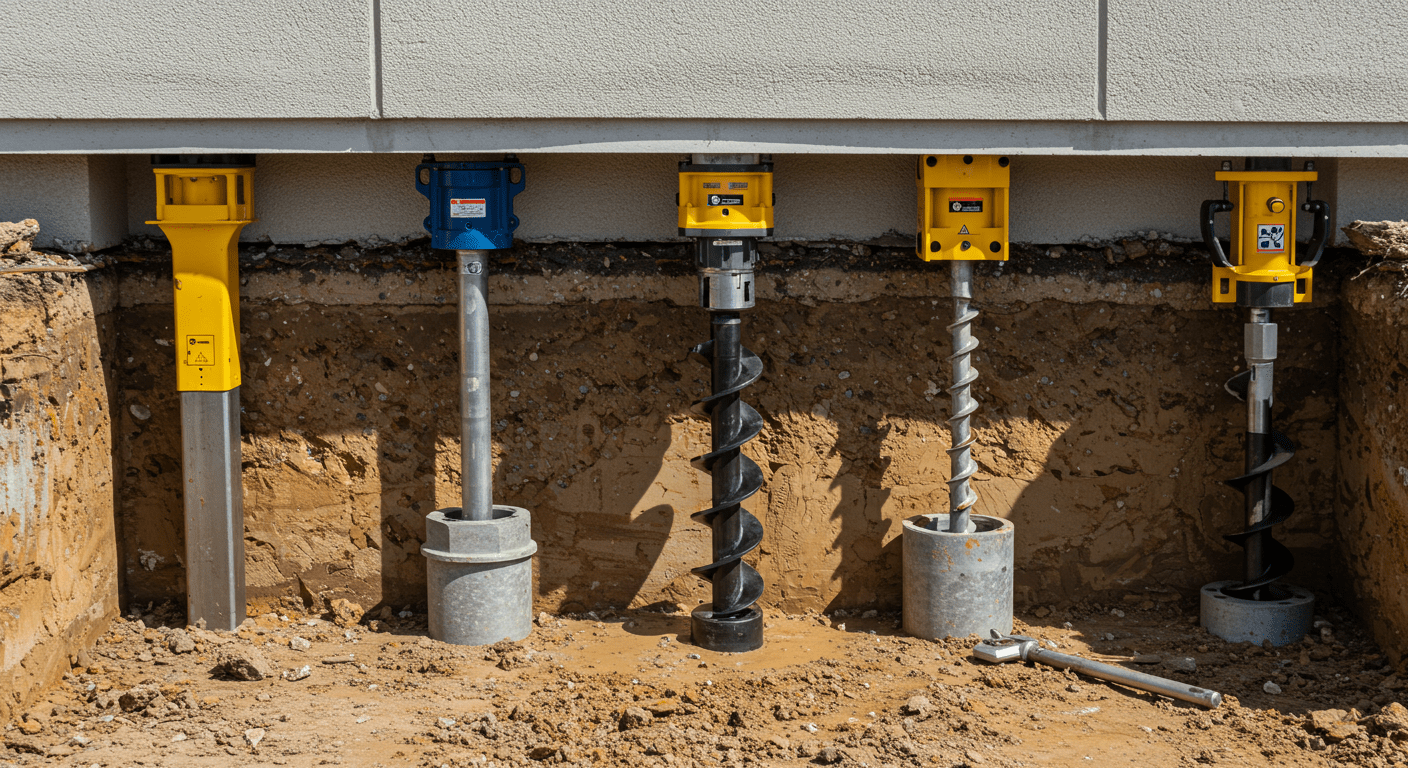
Adaptability to Site-Specific Conditions:
Conclusion
In the battle against the challenges posed by expansive soils, helical piers emerge as a strategic and effective solution. Their ability to anchor into stable soil layers, resist vertical and lateral movements, distribute loads evenly, and minimize soil disturbance makes them a preferred choice for engineers facing the complexities of expansive soil conditions. With helical piers, construction projects can stand firm and resilient, even in regions where expansive soils might otherwise pose a significant threat to the integrity of foundations.